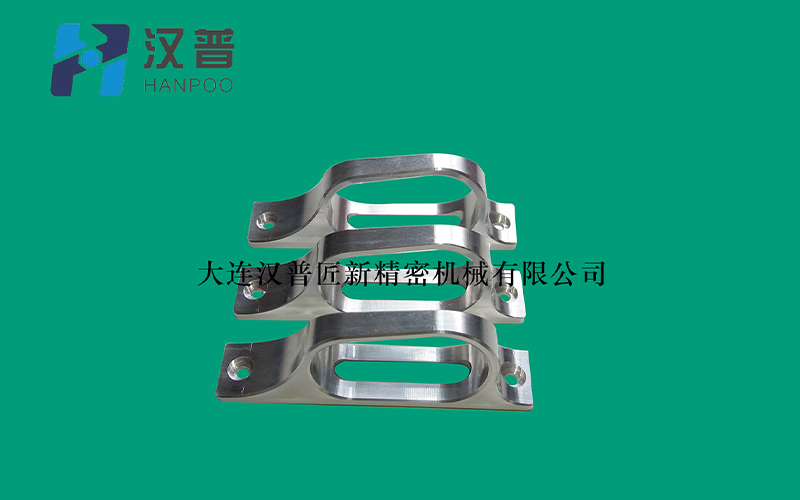
The so-called anodizing of aluminum is an electrolytic oxidation process in which the surfaces of aluminum and aluminum alloys are usually converted into an oxide film that has protective, decorative, and other functional properties. Anodizing of aluminum from this definition involves only the process of producing an anodizing film.
Metal or alloy parts are used as the anode to form oxide films on the surface by electrolysis. Metal oxide film changes the surface state and performance, such as surface coloring, improve corrosion resistance, enhance wear resistance and hardness, protect the metal surface. For example, aluminum anodic oxidation, aluminum and its alloys are placed in the corresponding electrolyte (such as sulfuric acid, chromic acid, oxalic acid, etc.) as the anode, under specific conditions and impressed current action, electrolysis. Anodic aluminum or its alloys are oxidized to form a thin layer of alumina on the surface, with a thickness of 5 ~ 30 microns and a hard anodic oxide film of 25 ~ 150 microns. Anodized aluminum or its alloy, improve its hardness and wear resistance, up to 250 ~ 500 kg/m2 mm, good heat resistance, hard anodized film melting point up to 2320K, excellent insulation, breakdown voltage up to 2000V, enhanced corrosion resistance, in the heat =0.03NaCl salt spray after thousands of hours of corrosion. The thin layer of oxide film has a large number of micro-pores, which can absorb various lubricants, and is suitable for the manufacture of engine cylinders or other wear-resistant parts. Film micro - pore adsorption ability can be colored into a variety of beautiful and gorgeous colors. Non-ferrous metals or their alloys (such as aluminum, magnesium and their alloys) can be anodized. This method is widely used in mechanical parts, aircraft and automotive parts, precision instruments and radio equipment, household goods and architectural decoration.



 Page location :
Page location : 



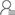 Contacts:General manager Zheng
Contacts:General manager Zheng Tel:+86-411-6687-9288
Tel:+86-411-6687-9288 Address:No.3Buliding No.3 HuaiHe Zhong Road DDA Dalian City Liaoning Province P.R.China
Address:No.3Buliding No.3 HuaiHe Zhong Road DDA Dalian City Liaoning Province P.R.China


